What Are CFDs? How Do CFDs Work?


How Do CFDs Work: Understanding Contracts for Difference
If you’re new to the world of trading and investing, you might have come across the term “CFDs” and wondered, “How do CFDs work?” Well, you’re in the right place. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll demystify the concept of Contracts for Difference (CFDs) and shed light on how they operate in the financial markets.
What Are CFDs?
Before diving into the mechanics of CFDs, let’s start with a simple definition. A CFD, or Contract for Difference, is a financial instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of various assets, such as stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices, without owning the underlying asset itself. It’s a popular derivative product that offers traders the opportunity to profit from both rising and falling markets.
The Mechanics: How Do CFDs Work?
Now that we’ve defined CFDs, let’s explore how they actually work. CFDs operate on the principle of mirroring the price movements of the underlying asset. When you open a CFD trade, you enter into a contract with a broker, agreeing to exchange the difference in the price of the asset between the opening and closing of the trade.
Leverage: Amplifying Your Trading Potential
One of the key features of CFD trading is the ability to utilize leverage. Leverage allows traders to open positions with a fraction of the total trade value, which means you can control larger positions with a relatively smaller initial investment. For example, with a leverage of 1:10, you only need to put down $1,000 to control a position worth $10,000. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it’s essential to remember that it also magnifies potential losses, so risk management is crucial.
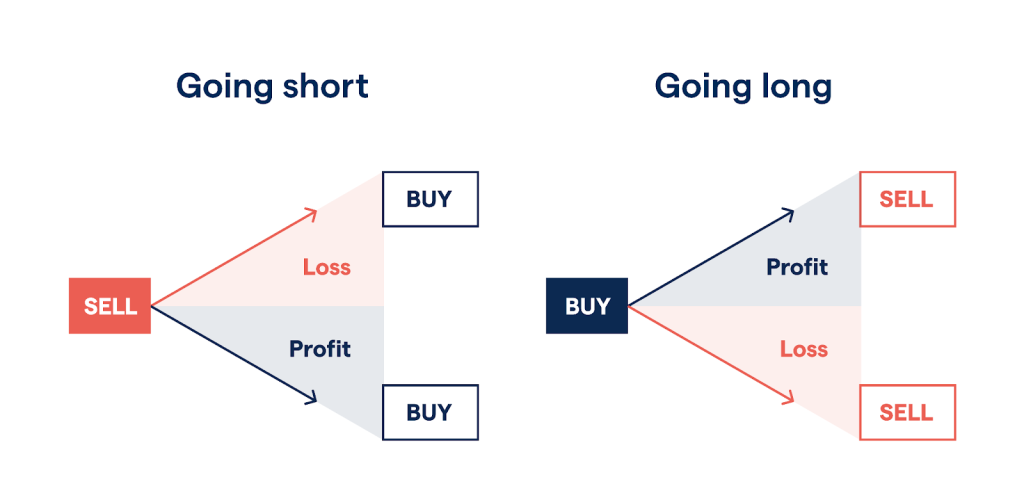
Going Long or Short: Profiting from Rising and Falling Markets
Unlike traditional forms of investment, such as buying stocks, where you profit only if the price increases, CFDs enable you to speculate on both rising and falling markets. If you believe the price of an asset will rise, you can open a “Long” position and profit from the upward movement. Conversely, if you anticipate a decline in the asset’s value, you can open a “Short” position and profit from the downward movement. This flexibility is one of the reasons why CFDs have gained popularity among traders.
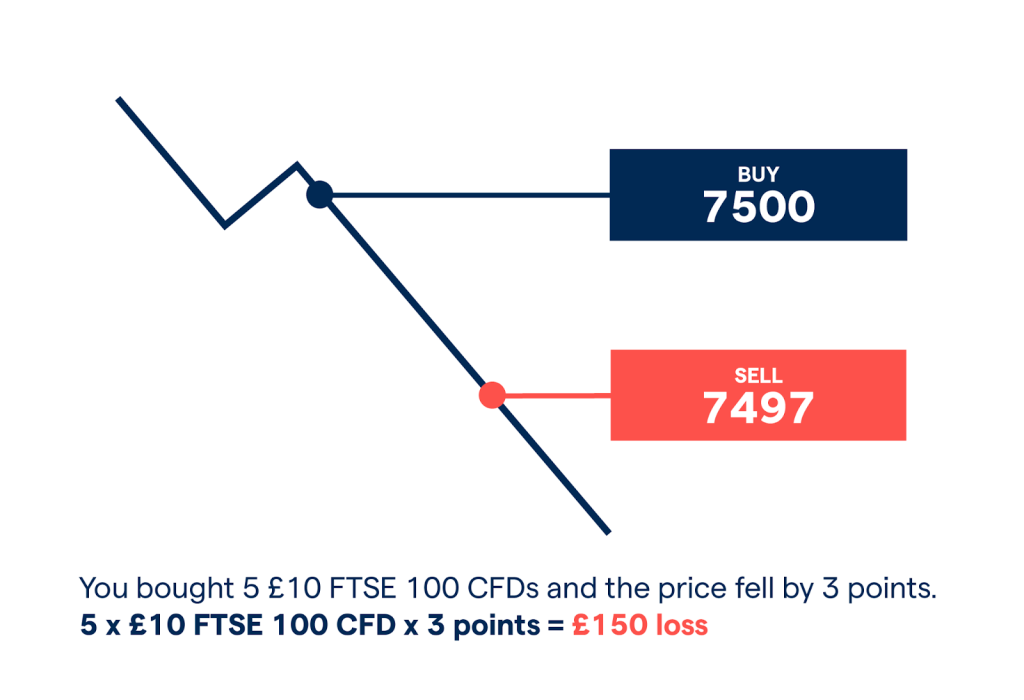
Risk and Reward: Calculating Profits and Losses
When trading CFDs, it’s essential to understand the potential risks and rewards involved. The profit or loss from a CFD trade is determined by the difference between the opening and closing prices, multiplied by the number of CFD units. If the market moves in your favor, you make a profit; if it moves against you, you incur a loss. It’s crucial to set stop-loss and take-profit levels to manage risk and protect your capital.

Market Access: Diversify Your Trading Portfolio
One of the advantages of CFD trading is the wide range of markets you can access. From stocks and commodities to currencies and indices, CFDs allow you to diversify your trading portfolio and explore various market opportunities. This flexibility empowers traders to adapt to different market conditions and take advantage of global economic trends.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Potential of CFD Trading
In conclusion, CFDs provide traders with a flexible and accessible way to participate in the financial markets. By speculating on the price movements of various assets without owning them, traders can potentially profit from both rising and falling markets. However, it’s important to remember that CFD trading involves risks, and thorough risk management is crucial. With a solid understanding of how CFDs work and a disciplined approach to trading, you can unlock the potential of this exciting financial instrument.
