What is a Credit Swap?


What is a Credit Swap? A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding this Financial Instrument
If you’ve ever delved into the world of finance, you may have come across the term “credit swap.” It’s one of those financial buzzwords that can leave even seasoned traders scratching their heads. In this article, we will demystify the concept of credit swaps and provide you with a beginner’s guide to understanding this complex financial instrument.
Understanding Credit Swaps
At its core, a credit swap is a financial agreement between two parties that allows them to exchange the credit risk associated with a particular asset or liability. This agreement acts as a form of insurance, offering protection against potential default or adverse credit events.
The Problem:
Imagine you lend a substantial amount of money to a company, expecting a steady stream of interest payments over time. However, as time passes, you begin to worry about the company’s financial stability and the possibility of default. You want to mitigate this risk without completely divesting from the investment. This is where a credit swap comes into play.
The Solution: Enter the Credit Swap
A credit swap serves as a risk management tool, enabling you to transfer the credit risk associated with your investment to another party, typically a financial institution or an investor willing to take on that risk. In exchange for this protection, you agree to pay them a regular fee or “premium.”
How does a Credit Swap work?
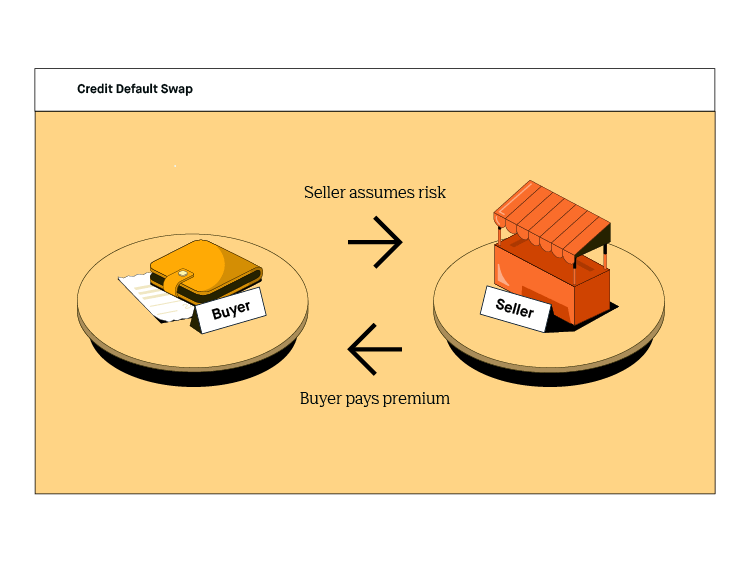
In a credit swap, there are two primary roles: the protection buyer and the protection seller. Let’s break it down:
- Protection Buyer: The party seeking to transfer the credit risk is known as the protection buyer. They hold the asset or investment that is subject to credit risk and is looking to minimize potential losses.
- Protection Seller: The protection seller, on the other hand, is willing to assume the credit risk. They provide insurance against default or credit events and receive the premium payments from the protection buyer.

Benefits and Risks
Credit swaps can provide various benefits, such as allowing investors to diversify their portfolios, manage risk exposure, and hedge against potential losses. They offer a flexible and customizable way to navigate the complex world of credit risk. However, it’s essential to recognize that credit swaps also carry their own set of risks. If the protection seller fails to fulfill their obligations, the protection buyer may not receive the expected compensation in the event of a credit event. Furthermore, credit swaps are subject to market fluctuations and can involve counterparty risk.
Conclusion
Now that you have a basic understanding of what a credit swap is, you can start to appreciate its role in the financial landscape. Credit swaps act as a valuable tool for managing credit risk, providing investors with a means to protect their investments and navigate uncertain market conditions. Remember, while credit swaps offer opportunities for risk management, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research, seek expert advice, and carefully assess the terms and conditions of any credit swap agreement before engaging in such transactions. With the right knowledge and caution, credit swaps can be a powerful instrument to navigate the dynamic world of finance.